3 Treatment Options for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare but serious blood disorder that can significantly impact a person’s health and daily life. Understanding effective PNH strategies is crucial for managing this condition and improving patients’ quality of life. This blog will explore the symptoms of PNH, various treatment options available, and guidelines for managing this complex disorder, aiming to provide clear and helpful information for those affected.
What is Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria?
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria is a blood disorder that arises from a mutation in the bone marrow. This mutation affects the production of red blood cells, making them more vulnerable to destruction by the body’s immune system. As a result, patients experience hemolysis, a process where red blood cells break down faster than the body can produce new ones, leading to a shortage of healthy red blood cells.
The name of the disorder highlights a key symptom: hemoglobin, which is a protein in red blood cells, can leak into the urine after red blood cells are destroyed. This often results in dark or cola-colored urine, especially during the night, when hemolysis tends to occur more frequently. PNH is considered rare, affecting approximately 1 to 2 people per million each year. Due to its complexity, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to manage symptoms and prevent serious complications.
What are the Symptoms of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria?
The symptoms of PNH can vary widely among individuals, but many experience similar issues that can severely affect their quality of life. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Many patients suffer from extreme tiredness, which is often due to anemia—a condition caused by a lack of healthy red blood cells. This fatigue can make daily activities feel overwhelming and unmanageable.
- Dark Urine: One of the hallmark symptoms of PNH, the urine may appear dark or red, particularly in the morning after a night of hemolysis. This can be alarming for patients and is an important symptom to report to healthcare providers.
- Abdominal Pain: Some individuals may experience discomfort or pain in the abdomen, which can be linked to complications such as blood clots forming in the blood vessels.
- Blood Clots: Patients with PNH are at increased risk for thrombosis, which can lead to serious conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. Recognizing the signs of blood clots is vital for timely intervention.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical exertion, can occur as a result of reduced oxygen levels in the blood due to anemia. This symptom can significantly limit physical activities and overall quality of life.
Identifying these symptoms early can help individuals seek medical advice and initiate appropriate treatment, improving their health outcomes.
PNH Treatment Strategies
Managing PNH effectively involves a combination of treatment strategies tailored to each patient’s needs. The primary goals are to reduce hemolysis, improve symptoms, and enhance the overall quality of life. Here are some key treatment options:
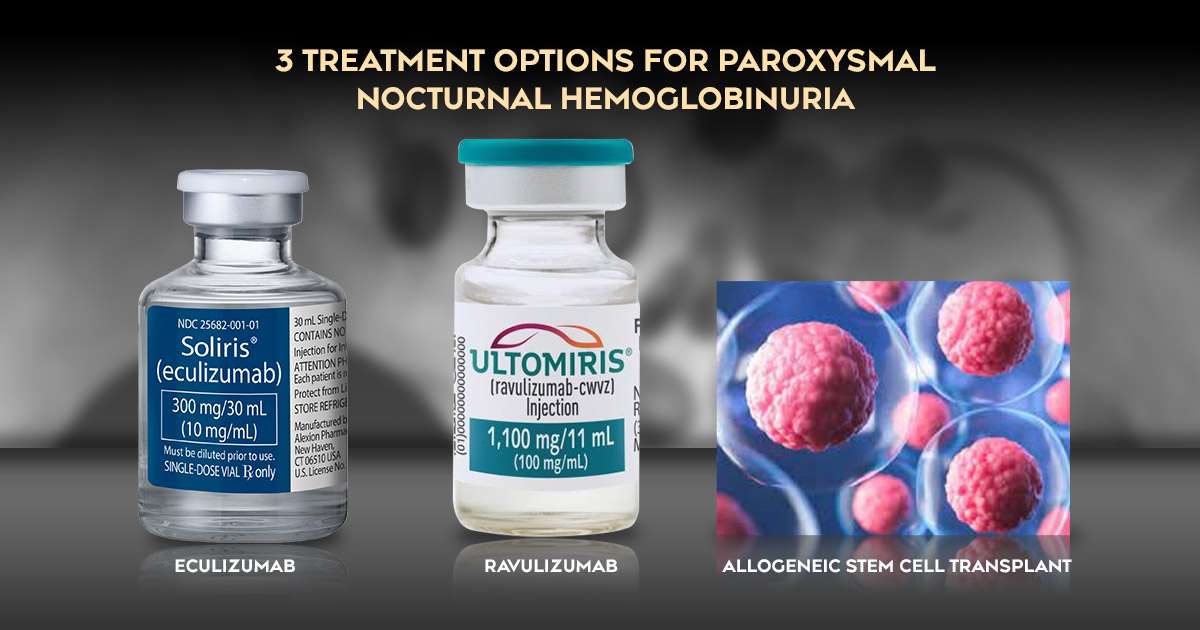
Eculizumab
Eculizumab is a complement inhibitor that has revolutionized the treatment landscape for PNH. It works by blocking the complement system, a part of the immune system that mistakenly attacks red blood cells in PNH patients. Clinical studies have shown that eculizumab can significantly reduce hemolysis and improve symptoms, allowing many patients to lead a more normal and fulfilling life. However, it is important to note that this medication is quite expensive and requires regular intravenous infusions, typically every two weeks.
Ravulizumab
Ravulizumab is another complement inhibitor similar to eculizumab, but it has a longer-lasting effect, allowing for less frequent dosing. This can enhance convenience for patients, as they may only need infusions every eight weeks instead of biweekly. Research indicates that ravulizumab effectively treats PNH, providing relief from symptoms and reducing hemolysis, similar to eculizumab. This option may improve adherence to treatment plans and overall patient satisfaction.
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant
For some patients, especially those with severe PNH or those who do not respond well to available therapies, an allogeneic stem cell transplant may be considered. This procedure involves replacing the patient’s bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor. While this treatment has the potential to cure PNH, it carries significant risks, including infections and complications related to the transplant process. Therefore, careful evaluation and counseling are essential before considering this option.
Are There Alternative Treatments for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria?
In addition to standard therapies, some patients explore alternative treatments for PNH. These may include lifestyle changes, nutritional support, and complementary therapies. Some studies suggest that certain dietary adjustments—such as increasing intake of specific vitamins or minerals—may help manage symptoms, although more research is needed in this area. Some individuals may also consider acupuncture, mindfulness practices, or herbal supplements, but it is crucial for patients to discuss any alternative treatments with their healthcare provider to ensure they safely complement existing therapies.
How is it Diagnosed?
Diagnosing PNH typically involves several tests to confirm the presence of the disorder and assess its severity. A complete blood count (CBC) is often the first step, checking for signs of anemia and other blood-related issues. Flow cytometry is a specialized test that can definitively confirm PNH by examining the characteristics of blood cells. This test looks for the absence of specific markers on red blood cells, indicating a defect caused by the disorder. Regular follow-ups and monitoring are vital to track disease progression and the effectiveness of treatments, ensuring timely interventions when necessary.
Short PNH Treatment Guidelines to Follow
Following specific guidelines can significantly improve the management of PNH. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Regular Monitoring: Patients should have regular check-ups with their healthcare provider to monitor blood counts and assess the effectiveness of treatments. Keeping a close eye on symptoms can help in early detection of complications.
- Prompt Treatment of Symptoms: Addressing symptoms such as fatigue and abdominal pain can greatly enhance the quality of life. Patients should communicate openly with their doctors about any changes in their condition.
- Education: Patients and their caregivers should be educated about the disease, its symptoms, and management options. Understanding PNH can empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
- Emergency Care: Recognizing signs of complications, such as blood clots or severe abdominal pain, is essential for timely intervention. Patients should be aware of when to seek emergency care.
- Psychosocial Support: Living with a chronic condition can be challenging, so support groups and counseling can help patients cope with the emotional aspects of PNH. Connecting with others who understand the experience can be invaluable.
Choosing the Right PNH Treatment Strategy
Understanding PNH strategies is vital for managing this rare and complex blood disorder. Treatments like eculizumab and ravulizumab have significantly improved the landscape for many patients, providing relief from symptoms and enhancing overall well-being. While traditional therapies are essential, exploring alternative treatments and lifestyle modifications can also contribute to better management of PNH. Regular monitoring and adherence to treatment guidelines are crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes. With the right approach and support, individuals living with PNH can lead fulfilling lives, overcoming the challenges posed by this condition.

